News
November 29, 2025
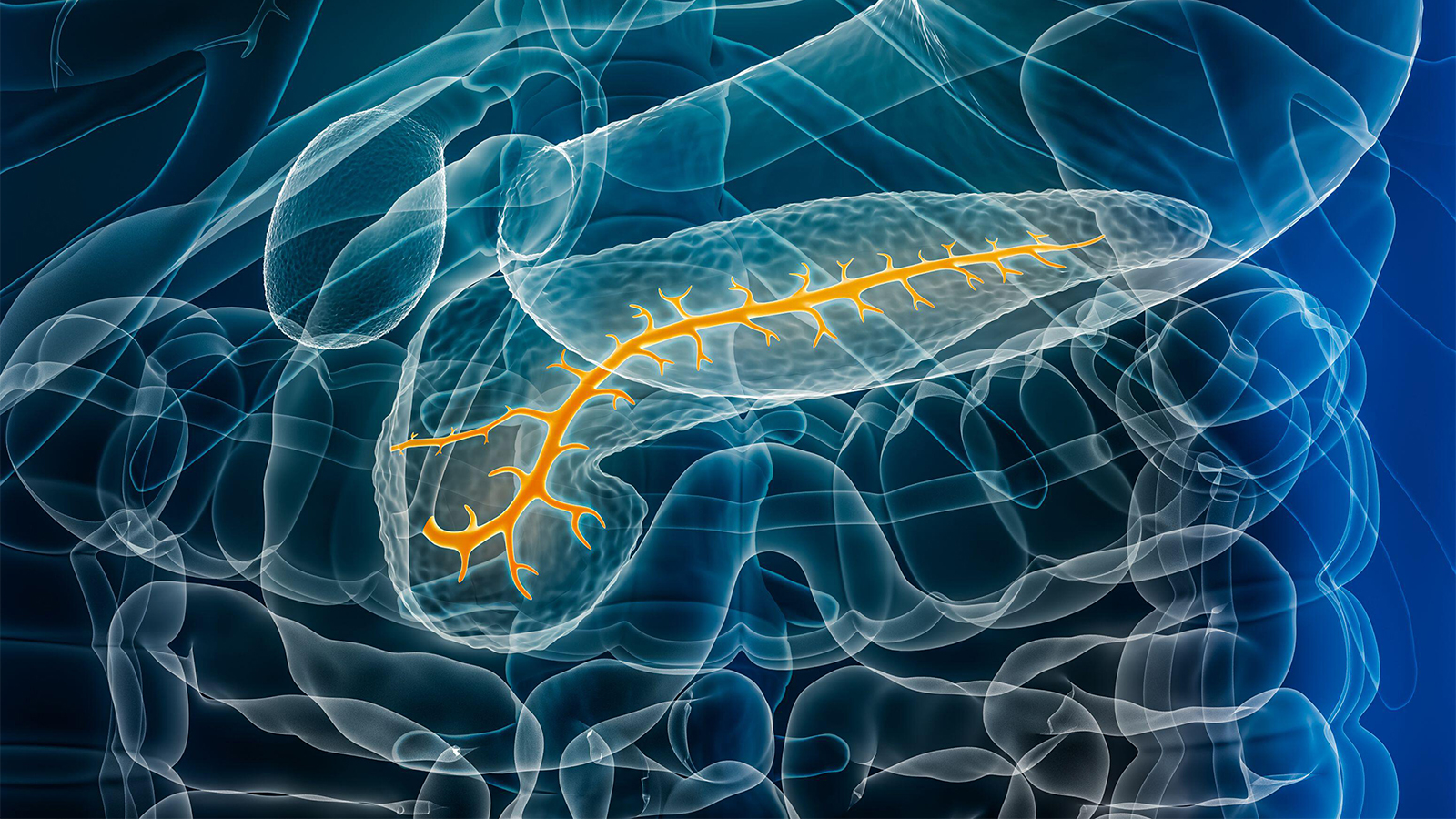
Study Finds New Risk Factor for Pancreatic Cancer
(MedPage Today) -- Mild dilatation of the main pancreatic duct, even without an obvious mass, is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer in high-risk individuals, according to data from a prospective cohort study.Among 641 high-risk individuals with...
**Study Finds New Risk Factor for Pancreatic Cancer**
A recent study has uncovered a potential new warning sign for pancreatic cancer, offering hope for earlier detection and treatment for those at high risk. The research, published in *MedPage Today*, suggests that even a slight widening of the main pancreatic duct, the tube that carries digestive fluids from the pancreas, can be a significant risk factor, even in the absence of a visible tumor.
Pancreatic cancer is notoriously difficult to detect in its early stages, often leading to late diagnoses and poorer outcomes. This new finding could change the way doctors monitor individuals known to be at higher risk of developing the disease.
The prospective cohort study followed 641 high-risk individuals. These individuals likely had factors increasing their susceptibility to pancreatic cancer, such as a family history of the disease, genetic predispositions, or other relevant medical conditions. The study focused on identifying subtle indicators that might precede the development of a full-blown tumor.
Researchers discovered that mild dilatation, or widening, of the main pancreatic duct was significantly correlated with an increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer. This is crucial because previous diagnostic efforts have primarily focused on identifying distinct masses or tumors within the pancreas. The study suggests that focusing only on tumors could be missing earlier, more subtle signs of the disease.
While the study highlights a promising new avenue for early detection, experts caution that further research is needed. It's important to note that not everyone with a slightly widened pancreatic duct will develop pancreatic cancer. However, this finding offers a valuable new piece of the puzzle, helping doctors to better assess risk and potentially intervene earlier in high-risk individuals.
The implications of this study are significant. By incorporating the assessment of pancreatic duct size into screening protocols for high-risk individuals, healthcare professionals may be able to identify and monitor those who are at a greater risk, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses, more effective treatments, and ultimately, improved survival rates for patients with pancreatic cancer. This finding underscores the importance of ongoing research and proactive screening strategies in the fight against this challenging disease.
A recent study has uncovered a potential new warning sign for pancreatic cancer, offering hope for earlier detection and treatment for those at high risk. The research, published in *MedPage Today*, suggests that even a slight widening of the main pancreatic duct, the tube that carries digestive fluids from the pancreas, can be a significant risk factor, even in the absence of a visible tumor.
Pancreatic cancer is notoriously difficult to detect in its early stages, often leading to late diagnoses and poorer outcomes. This new finding could change the way doctors monitor individuals known to be at higher risk of developing the disease.
The prospective cohort study followed 641 high-risk individuals. These individuals likely had factors increasing their susceptibility to pancreatic cancer, such as a family history of the disease, genetic predispositions, or other relevant medical conditions. The study focused on identifying subtle indicators that might precede the development of a full-blown tumor.
Researchers discovered that mild dilatation, or widening, of the main pancreatic duct was significantly correlated with an increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer. This is crucial because previous diagnostic efforts have primarily focused on identifying distinct masses or tumors within the pancreas. The study suggests that focusing only on tumors could be missing earlier, more subtle signs of the disease.
While the study highlights a promising new avenue for early detection, experts caution that further research is needed. It's important to note that not everyone with a slightly widened pancreatic duct will develop pancreatic cancer. However, this finding offers a valuable new piece of the puzzle, helping doctors to better assess risk and potentially intervene earlier in high-risk individuals.
The implications of this study are significant. By incorporating the assessment of pancreatic duct size into screening protocols for high-risk individuals, healthcare professionals may be able to identify and monitor those who are at a greater risk, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses, more effective treatments, and ultimately, improved survival rates for patients with pancreatic cancer. This finding underscores the importance of ongoing research and proactive screening strategies in the fight against this challenging disease.
Category:
Politics