News
October 19, 2025
ISRO’s Lunar Orbiter Chandrayaan-2 Detects Solar Impact on Moon’s Atmosphere
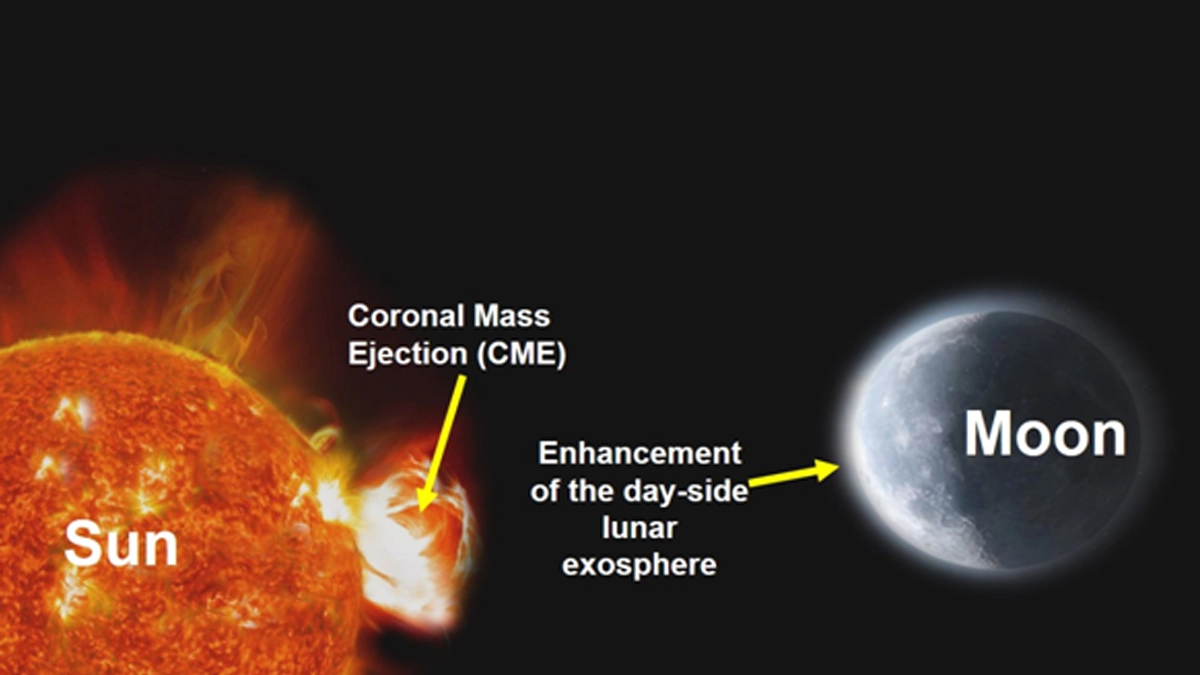
The observation was made using the Chandra’s Atmospheric Composition Explorer-2 (CHACE-2) instrument onboard the orbiter. During a rare solar event on May 10, 2024, a series of CMEs impacted the Moon, leading to a significant increase in the total pressure of the dayside lunar exosphere — the extremely thin atmosphere surrounding the Moon.
**ISRO's Lunar Orbiter Chandrayaan-2 Detects Solar Impact on Moon’s Atmosphere**
In a significant scientific achievement, India's Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter has detected the impact of a solar event on the Moon's extremely thin atmosphere, known as the exosphere. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that the observations were made using the Chandra's Atmospheric Composition Explorer-2 (CHACE-2) instrument, which is a key payload onboard the orbiter.
The rare solar event occurred on May 10, 2024, when a series of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) – large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun – slammed into the Moon. These CMEs, essentially powerful solar winds, interacted with the lunar environment in a way that significantly altered the composition and pressure of the exosphere.
The CHACE-2 instrument meticulously recorded a substantial increase in the total pressure of the dayside lunar exosphere as a direct consequence of the solar impact. The data collected provides valuable insights into how solar activity influences the lunar environment, a topic of great interest to scientists studying space weather and its effects on celestial bodies.
The lunar exosphere is incredibly sparse, far less dense than Earth's atmosphere. It's composed of neutral atoms and molecules that are constantly being released from the lunar surface due to various processes, including solar wind sputtering, micrometeoroid impacts, and thermal desorption. Understanding the dynamics of this exosphere is crucial for several reasons.
Firstly, it helps scientists unravel the processes that shape the lunar surface. Secondly, it provides information about the Moon's volatile inventory, including water ice that may be trapped in permanently shadowed craters. Finally, studying the exosphere's response to solar events like the one observed provides a better understanding of space weather effects throughout the solar system.
The Chandrayaan-2 mission, although its lander mission faced challenges, continues to provide invaluable data from its orbiter, significantly contributing to our understanding of the Moon and its interaction with the space environment. The latest findings from the CHACE-2 instrument are a testament to the mission's ongoing success and the importance of continued lunar exploration. This observation will undoubtedly contribute to more accurate models of lunar exosphere behavior and enhance our understanding of space weather’s reach.
In a significant scientific achievement, India's Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter has detected the impact of a solar event on the Moon's extremely thin atmosphere, known as the exosphere. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced that the observations were made using the Chandra's Atmospheric Composition Explorer-2 (CHACE-2) instrument, which is a key payload onboard the orbiter.
The rare solar event occurred on May 10, 2024, when a series of coronal mass ejections (CMEs) – large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun – slammed into the Moon. These CMEs, essentially powerful solar winds, interacted with the lunar environment in a way that significantly altered the composition and pressure of the exosphere.
The CHACE-2 instrument meticulously recorded a substantial increase in the total pressure of the dayside lunar exosphere as a direct consequence of the solar impact. The data collected provides valuable insights into how solar activity influences the lunar environment, a topic of great interest to scientists studying space weather and its effects on celestial bodies.
The lunar exosphere is incredibly sparse, far less dense than Earth's atmosphere. It's composed of neutral atoms and molecules that are constantly being released from the lunar surface due to various processes, including solar wind sputtering, micrometeoroid impacts, and thermal desorption. Understanding the dynamics of this exosphere is crucial for several reasons.
Firstly, it helps scientists unravel the processes that shape the lunar surface. Secondly, it provides information about the Moon's volatile inventory, including water ice that may be trapped in permanently shadowed craters. Finally, studying the exosphere's response to solar events like the one observed provides a better understanding of space weather effects throughout the solar system.
The Chandrayaan-2 mission, although its lander mission faced challenges, continues to provide invaluable data from its orbiter, significantly contributing to our understanding of the Moon and its interaction with the space environment. The latest findings from the CHACE-2 instrument are a testament to the mission's ongoing success and the importance of continued lunar exploration. This observation will undoubtedly contribute to more accurate models of lunar exosphere behavior and enhance our understanding of space weather’s reach.
Category:
Technology