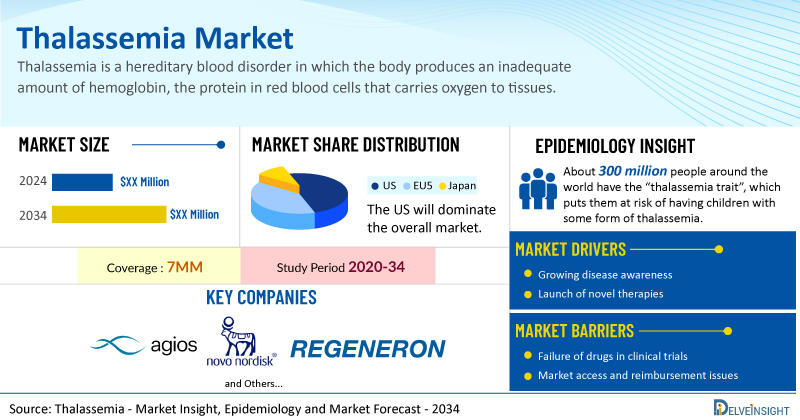
Thalassemia Treatment Market to Witness Significant Growth by 2034 Driven by Novel Drug Development | DelveInsight
The thalassemia market is primarily driven by regular blood transfusions and iron chelation therapies, which help manage anemia and prevent iron overload. Curative treatments, such as stem cell transplants, remain constrained due to limited donor availability. While there are currently no approved drugs for alpha thalassemia, several therapies are available for beta thalassemia, including CASGEVY, ZYNTEGLO, and REBLOZYL. Novel treatments like PYRUKYND, designed to reduce the need for transfusions, are anticipated to transform the long-term management of the disease. The thalassemia market is primarily driven by regular blood transfusions and iron chelation therapies, which help manage anemia and prevent iron overload. Curative treatments, such as stem cell transplants, remain constrained due to limited donor availability. While there are currently no approved drugs for alpha thalassemia, several therapies are available for beta thalassemia, including CASGEVY, ZYNTEGLO, and REBLOZYL. Novel treatments like PYRUKYND, designed to reduce the need for transfusions, are anticipated to transform the long-term management of the disease.
Thalassemia, characterized by the body's inability to produce enough hemoglobin, often necessitates regular blood transfusions to manage anemia. These transfusions, while life-saving, can lead to iron overload, requiring patients to undergo iron chelation therapy to remove excess iron from their bodies. These two approaches currently form the backbone of thalassemia management.
However, the landscape is shifting. Stem cell transplants offer a potential cure, but their widespread use is hampered by the difficulty in finding suitable donors. This limitation underscores the urgent need for alternative and more accessible treatment options.
While no drugs are currently approved specifically for alpha thalassemia, significant strides have been made in treating beta thalassemia, the other main type of the condition. Existing therapies like CASGEVY, ZYNTEGLO, and REBLOZYL provide valuable tools for managing the disease.
Looking ahead, the introduction of novel treatments like PYRUKYND promises to revolutionize thalassemia care. This drug is specifically designed to reduce the frequency of blood transfusions, a major burden for many patients. By minimizing the need for transfusions, PYRUKYND could significantly improve the long-term health and quality of life for individuals with thalassemia, while also mitigating the risks associated with iron overload and the logistical challenges of frequent hospital visits. The anticipated impact of such therapies is a key driver behind the projected growth in the thalassemia treatment market over the next decade. The market is expected to see significant investment and development as researchers and pharmaceutical companies strive to bring more effective and accessible treatments to patients worldwide.